{{ i18n.t(promptHeader) }}
Game settings
Reference Cards (38)
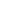
+=
Function
A function gives a name to a set of blocks. Once a function is defined, it can be used many times in the code. You can use the functions from other sprites. When in another sprite, the function block is defined in the Other objects' Functions library.
Appears in tab: Control
>
The operator > compares the values on both of its sides. The result is true (yes) when the value on its left is greater than the value on its right.
Appears in tab: Operators
counter.value
A property of the Counter widget. The property named value holds the value of the Counter.
Appears in tab: WIDGETS
-=
Counter widget
The Counter widget is used to keep count and can be displayed in the game.
Appears in tab: WIDGETS
onCollideWithTilemap definition
A property of a Sprite object that acts as an event handler. If onCollideWithTilemap is set equal to a function, that function is called any time the sprite collides with any tile. The function takes no arguments and does not distinguish which tile type was collided with.
Appears in tab: Events
else
An else statement follows an if statement. If the condition in the if statement is false (no), then the code inside the else statement is executed.
Appears in tab: Control
destroy()
game.reset()
Resets the game.
<
The operator < compares the values on both of its sides. The result is true (yes) when the value on its left is smaller than the value on its right.
Appears in tab: Operators
getVelocityY()
text.text
onUpdate definition
A property of a Sprite object that acts as a special kind of event handler. If onUpdate is set equal to a function, that function is called every time the game screen redraws, usually 30 to 60 times per second. The onUpdate handler can be used control the sprite's behavior.
Appears in tab: Events
getVelocityX()
Text widget
The Text widget is used to display labels or texts on the game’s screen.
Appears in tab: WIDGETS
play()
onCollide definition
Creates an event handler for two sprites collide. The first argument is the name of the other sprite. The second argument is the function to be called when the two sprites touch.
Appears in tab: Events
Gravity
Defines the level of gravity in the game. Zero means that there is no gravity and the sprites do not fall down.
Appears in tab: GAME
Immovable
A property of the sprite. This option applies when two sprites collide. Check this option when a sprite should not move during a collision with another sprite. If a sprite is not immovable another sprite that runs into it can push it.
Appears in tab: SPRITES
Allow gravity
A property of the sprite. Defines if the sprite is affected by gravity (checked) or not (unchecked). This option applies only when the game has gravity. If the game has gravity and this box is checked - when running the game the sprite will fall until it reaches a surface (world boundary, tiles, or another sprite). If the box is unchecked, the sprite will not move upon running the game.
Appears in tab: SPRITES
World height
Sets the world’s height. The visible part of the world is 600 by 400.
Appears in tab: GAME
Sprite's X
A property of the sprite. The sprite’s initial x position.
Appears in tab: SPRITES
Sprite's Y
A property of the sprite. The sprite’s initial y position.
Appears in tab: SPRITES
Camera target
Defines which sprite to follow. This is useful if the game world is bigger than 600 by 400. When the target sprite moves, the game window will scroll to keep up with it.
Appears in tab: GAME
World width
Sets the world’s width. The visible part of the world is 600 by 400.
Appears in tab: GAME
rotateLeft()
Rotates the sprite to the left. The argument is the speed with which the sprite starts rotating. The sprite slows down automatically so it will not spin forever.
Appears in tab: Movement
rotateRight()
Rotates the sprite to the right. The argument is the speed with which the sprite starts rotating. The sprite slows down automatically so it will not spin forever.
Appears in tab: Movement
==
The operator == compares the values on both of its sides. The result is true (yes) when both values are exactly the same and false (no) otherwise.
Appears in tab: Operators
If
if blocks are used for decision making. If the condition is true (yes), then the code inside the if block is executed.
Appears in tab: Control
onKey property
A property of a Sprite object that acts as an event handler. If onKey is set equal to a function, that function is called each time a keyboard key is pressed. The argument to the function is a code that represents whatever keyboard key that was pressed. This function can be used to control elements of the game using the keyboard.
Appears in tab: Events
thrust()
Applies force that pushes the sprite towards the top of the screen. The argument is the amount of force. If the game world includes gravity, the argument must be large enough to overcome gravity or the sprite will not move.
Appears in tab: Movement
Sounds
A game object that represents a sound. The sound can be played using the Play block.
Appears in tab: SOUNDS
Sprite
A game object represented as an image on the screen at specific coordinates. Sprites also allow running animation, events and physics motion.
Appears in tab: SPRITES
Widget
A game object that displays information or interacts with the player.
Appears in tab: WIDGETS
Game
An object representing the game as a whole. Properties of the game object include the width and height of the game world, which sprite the game camera should follow, and the strength of gravity in the game world.
Appears in tab: GAME
Tilemap
A game object made up of individual square tiles. Tiles can be used to "draw" the game world. They take up space and stop sprites from moving through them.
x, y coordinates
The world has width (represented by the x coordinates) and height (represented by the y coordinates). Each sprite in the world has x and y coordinates that define its position. The top left corner of the game world has coordinates x = 0, y = 0 As you move to the right, the value of x get bigger; as you move down, the value of y gets bigger. The x and y coordinates are displayed in the top left corner and are changed as the mouse cursor is moved.

UNLOCK EVERYTHING
Block - Based Coding

Text - Based Coding

Python Courses





